Backtesting Low-Cap Strategies: From EDA to Execution
Strategy Backtesting for Low-Cap Solana Tokens
Trading in low-cap Solana tokens is defined by asymmetry. The majority fail within minutes, but a minority deliver extreme multiples. The role of a systematic strategy is to cut exposure to the former and stay alive long enough to capture the latter.
This post documents how I used high-frequency data to explore entry and exit rules for my Low-Cap Solana Bot, and how I arrived at a configuration that balances profitability with survivability.
Dataset
The analysis begins with a dataset of 220+ tokens, each of which passed a proprietary alpha filter. For each token, I recorded:
- 15-second OHLCV candles for the first 30 minutes after detection.
- Market data: market cap, liquidity, trading volume.
- On-chain metrics: holder counts, buy/sell flows.
This focus on high-resolution, short-horizon data is deliberate: the majority of the edge in this market exists in the first minutes of trading.
Entry Logic: Filtering for Flow
Initial entry criteria captured too many tokens where sellers dominated. Exploratory analysis showed that buy/sell ratio is the most effective discriminator of genuine inflows.
- Threshold: ≥ 1.6 buys per sell in the 5-minute pre-entry window.
- Rationale: Stronger buy-side pressure correlates with higher probability of sustained price action.
-
Complementary filters:
- Minimum market cap → ensures enough depth to avoid excessive price impact.
- Minimum 5m volume and minimum number of buys → screens out illiquid traps.
- Maximum approval latency → avoids chasing tokens where momentum has already decayed.
These filters shift the entry universe from noise to tokens with measurable net demand.
Exit Logic: Introducing Timeouts
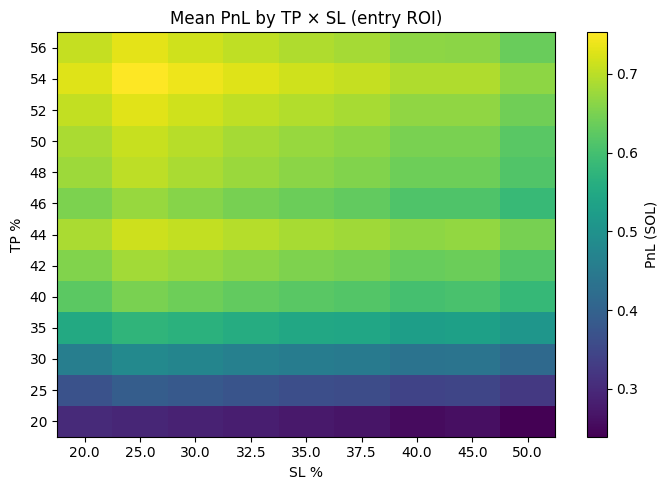
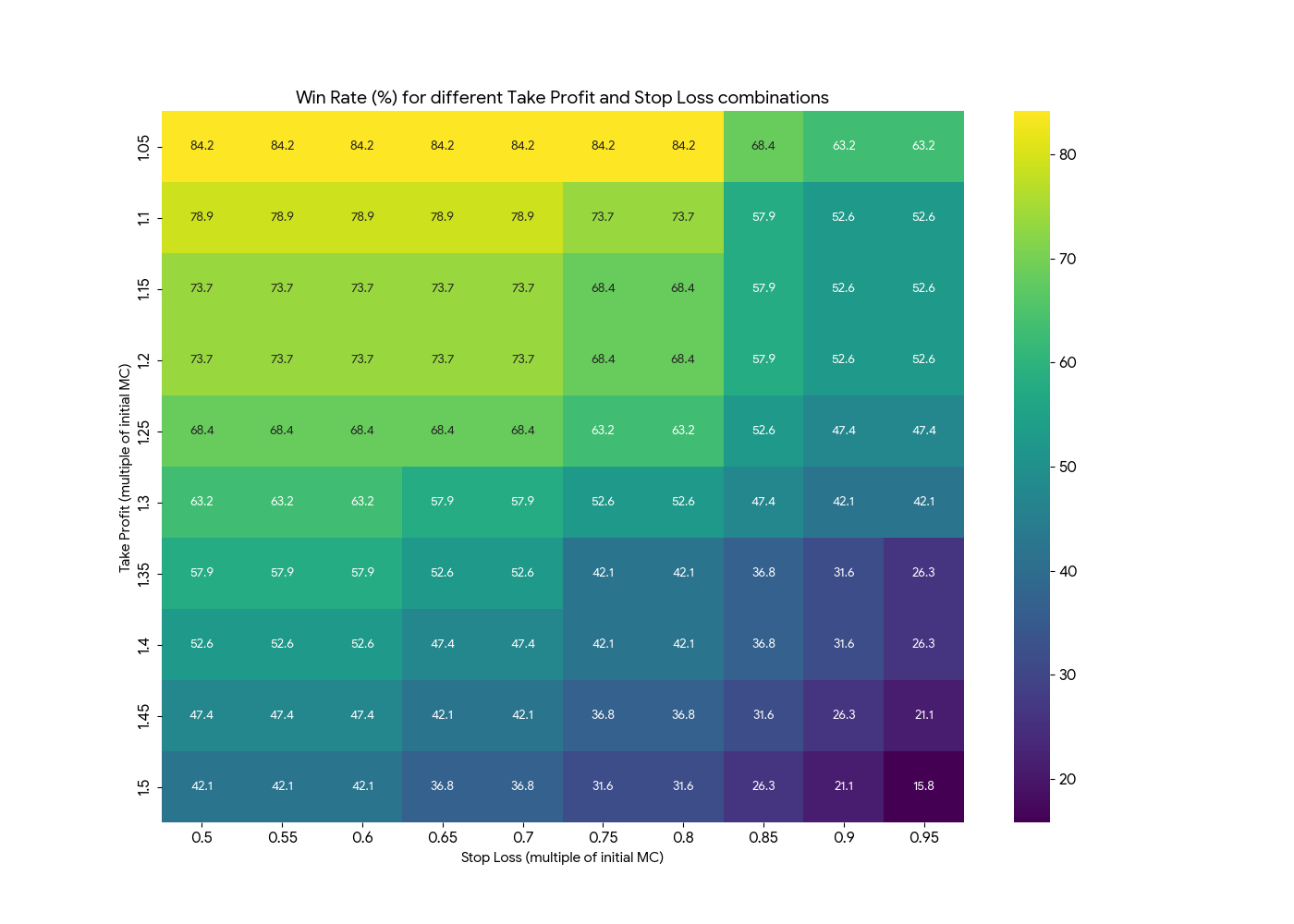
Early tests of take-profit (TP) and stop-loss (SL) rules revealed the classic trade-off:
- Tight exits (e.g., TP 20%, SL 10%) deliver win rates above 70% but low overall profitability.
- Loose exits (e.g., TP 200%, SL 70%) capture rare moonshots but suffer from poor expectancy.
The turning point was adding timeouts: automatic closure of positions after a fixed holding period.
- Observation: Most failed tokens collapse within the first 8 minutes.
- Implementation: A 6-minute timeout cuts dead trades while retaining exposure to early runners.
- Impact: Significantly reduced capital bleed in sideways or decaying tokens.
This single addition improved both expectancy and capital efficiency.
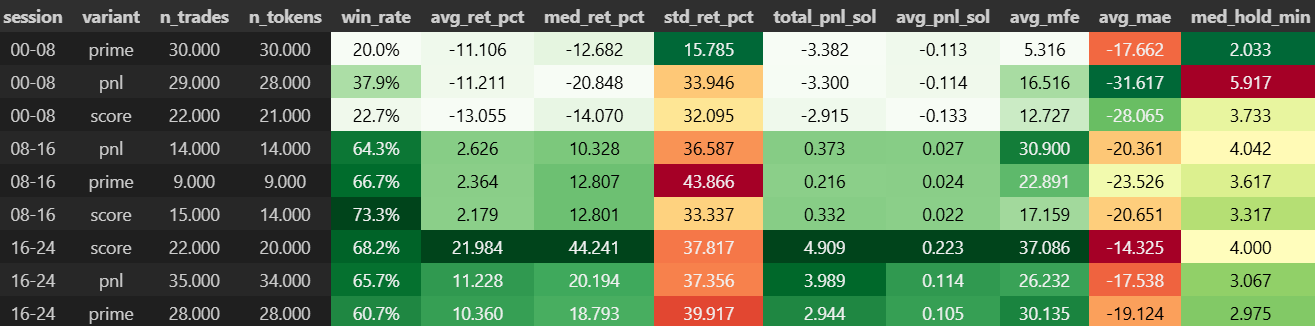
Exhaustive Grid Search
To avoid hindsight bias and overfitting, I structured the search as a systematic sweep of both entry and exit configurations.
Parameter Space
-
Entry Filters
- Market Cap Floor: 10k – 50k (increments of 5k)
- 5m Volume Floor: 10k – 60k (increments of 5k)
- Buy/Sell Ratio Threshold: 1.0 – 2.0 (increments of 0.05)
- Minimum Buys (5m): 1 – 10
- Approval Latency: capped at 2–4 minutes
-
Exit Rules
- Take Profit: 20% – 200% (increments of 10%)
- Stop Loss: 10% – 70% (increments of 5%)
- Timeout: 2 – 10 minutes (increments of 1 minute)
- Trailing Stop Loss: optional, 5% – 20% trailing bands
Evaluation Metrics
- Win Rate (WR): proportion of trades exiting positive.
- Profit Factor: ratio of gross profits to gross losses.
- Expectancy: average return per trade, adjusted for losers.
- PnL Distribution: dispersion of outcomes, to test for reliance on rare outliers.
- Time-in-Trade: average duration, to measure capital efficiency.
Scale of Search
- Hundreds of millions of configurations tested.
- Each configuration validated across 220+ tokens with 15-second bars.
- Retested on fresh token samples every few days to ensure robustness across regimes.
Key Insights
- Flow gates matter more than thresholds. Raising Buy/Sell ratio from 1.2 → 1.6 produced more uplift in expectancy than any single TP/SL tweak.
- Timeouts act as regime control. They truncate long-tail losses and reduce variance, especially in noisy liquidity conditions.
- Synergies dominate. Entry and exit rules interact; the best-performing strats were combinations, not individual parameter choices.
Trailing Exits
Trailing mechanisms provided an additional refinement:
- Trailing SL: ratchets upwards behind price, protecting gains if tokens extend.
- Partial TP + trailing remainder: locks partial profit, while leaving exposure to large runs.
While not always optimal as standalone exits, trailing rules smoothed equity curves and reduced variance when layered on top of the +50/–25/6m base strategy.
Current Optimal Strategy
The strategy currently deployed in the Low-Cap Solana Bot is:
- Entry: Buy/Sell ratio ≥ 1.6, with market cap and volume floors.
-
Exit:
- TP: +50% (full exit).
- SL: –25%.
- Timeout: 6 minutes.
- Optional trailing logic depending on regime.
This configuration is not static. I re-run the grid search and re-validate parameters every few days, ensuring the system adapts as liquidity conditions and volatility regimes change.
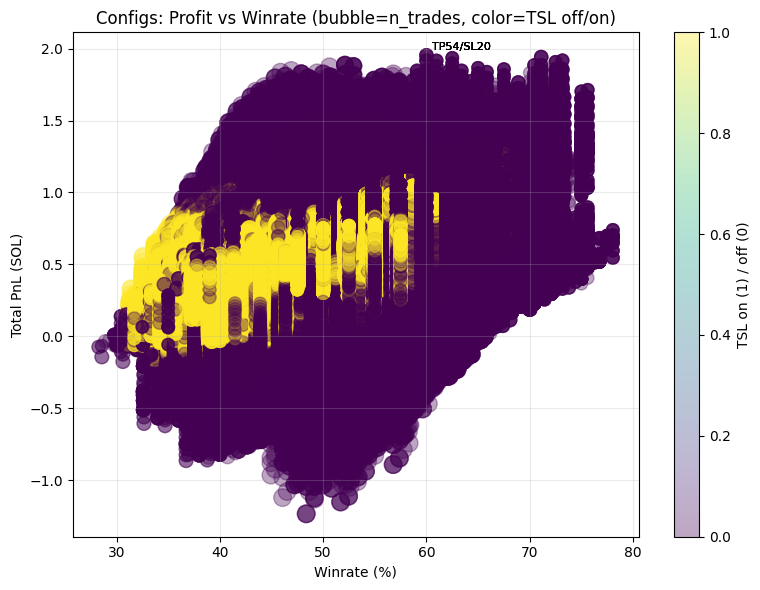
Exhaustive backtest of exit strategies across hundreds of millions of parameter combinations. Higher win rates concentrate around tighter take-profit and stop-loss bands, but with limited average returns.
Why This Works
- Flow-aware entry: Filters ensure positions are only opened when real buy pressure is present.
- Timeout discipline: Cuts capital drag from dead tokens, a frequent failure mode in microcaps.
- Balanced exits: The +50/–25 band captures a meaningful portion of winners while controlling losses.
- Adaptive overlays: Trailing logic provides incremental improvements in high-volatility conditions.
Closing Remarks
In low-cap Solana markets, edge comes not from predicting the next moonshot, but from building a systematic framework that cuts losers quickly, recycles capital, and stays alive long enough to capture the outliers.
The next post will step away from strategy results and focus on the system architecture of the Low-Cap Solana Bot: how the engine ingests new tokens, applies these filters, manages concurrency, and executes trades with low latency.